Data Loss Prevention: A Guide to Protecting Your Server
September 1, 20155 Things to Consider When Layering Security into Your Security Perimeter
Security is all over the news. Hilary’s emails, the Ashley Madison hack, Anthem Healthcare and even Minecraft have recently been compromised.
Security policies are crucial to protecting your data, but following protocol is even more important.
Accountability Questions Raised
Insider threat, intentional or not, is a sobering opportunity for data loss. And it’s not necessarily something, as in the case of Mrs. Clinton’s server, limited to endpoint devices, such as computers or mobile phones.
Hacking is not the kind of thing you want to happen—especially when brokering deals with foreign powers. What’s most disturbing is that someone at such a senior level, who should have known better, thought the security policies didn’t apply.
We will examine data loss prevention from a server security perspective and suggest 5 areas in which you can tighten your enterprise security.
Data Loss Defined
Tech Target says Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a strategy for making sure that end users do not send sensitive or critical information outside the corporate network. The term is also used to describe cyber security software products that help a network administrator control what data end users can transfer.
-
Assess Server Policies
First, as with the State Department situation, your enterprise must leverage complete control in the location of all servers. It therefore makes sense that your policy clearly states that all servers are deployed within the confines of an approved physical perimeter, such as a Data Center.
Further, each server must be owned and maintained by a specific operational group to maintain accountability, and configured according to approved guidelines.
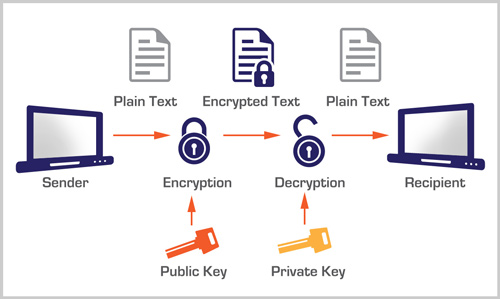
Encryption is essential to any data loss prevention protocol. It has been suggested that the breach in Anthem’s servers was because encryption may not have been employed within their servers as it is on information shared outside of them. 80 million individual’s personal information such as social security numbers, email addresses and medical ID numbers was stolen in the attack.
On the surface this might appear like common sense, but when you’re working with overworked engineers feeling management pressure and time constraints, surprises can happen.

-
Perform Regular Audits
Next, conduct periodic audits on current servers. Update their operating systems and security features such as encryption to measure and maintain the confidentiality of content. Don’t forget about your backups.
Server redundancy is a very simple way to ensure your data is safe.
Compliance audits should include the precise location, contact and backup contact for each server. Server contacts are easy to miss because if staff or vendors leave your company new contacts must be verified and distributed.

Note Inherent Vulnerabilities
- Database servers that include personal identity, health records and customer account information
- Applications servers may house unauthorized employee software downloads that introduce vulnerabilities
- Mail servers where employees can inadvertently leak classified information
-
Review Access and Employee Limits
A list of access rights for all people using your databases and servers must be maintained for each end user.
Sensitive information can be stored in network vaults and managed through a single access channel.
Regular Compliance Audits
- Account for access and log in history of privileged users
- Implement data encryption to layer access
- Use high resolution biometric scans and automated access keys

-
Deep Dive Monitoring Software
Algorithmic cyber security software is making huge strides in detecting risk, picking up things like changes in user behaviors. It monitors user profiles and logs things like work outside normal access hours, and IP address white/black lists.
It ranks risk based upon factors like geographic locations. It’s no secret that a large percentage of the hacks and attacks over the last five years come from Russia, the Ukraine and China.
One such tool is StratoKey, a cloud based application. Microsoft Exchange is another. There’s a host of great applications your enterprise can use. Depending upon the applications your currently using, you may be able to garner a deal if your monitoring software is part of a software suite.
-
Employee Training
If you saw the movie Black Hat with Chris Hemsworth, then you remember how the girlfriend used a thumb drive to inject a backdoor into the bad guy’s bank server, to find out who he was and find out how much money he had stashed.
But Social Engineering isn’t limited to USB sticks.
Other tactics include:
- Cloned websites that ask for login credentials
- Spear Phishing links in unsolicited emails
- Piggy Back Rides where the hacker pretends to have a heavy box and is granted access to a physical location because of human kindness.
All it takes is one unsuspecting employee and you could have a breach.
Hackers have been known to source bios to trick people into revealing passwords. This is an area where employee training is becoming as critical as firewall or other types of breach detection software.
Concluding Thoughts
The old adage—Rome was not built in a day—definitely applies when it comes to server integrity and data loss prevention. Regular compliance audits, clear policy statements posted, and periodic training close gaps and build in resistance.
Don’t give Lisbeth Salander an opportunity to compromise your data. Take a few smart steps that could cause a big problem.

